Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(六):GroupBy 数据分裂/应用/合并
文章目录
Pandas 系列文章:
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(一):认识 Pandas 及其 Series、DataFrame 对象
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(二):Index 索引对象以及各种索引操作
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(三):算术运算与缺失值的处理
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(四):函数应用、映射、排序和层级索引
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(五):统计计算与统计描述
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(六):GroupBy 数据分裂、应用与合并
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(七):合并数据集
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(八):数据重塑、重复数据处理与数据替换
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(九):时间序列
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Pandas(十):数据读写
专栏:
- NumPy 专栏:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/category_9780393.html
- Pandas 专栏:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/category_9780397.html
- Matplotlib 专栏:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/category_9780418.html
推荐学习资料与网站:
- NumPy 官方中文网:https://www.numpy.org.cn/
- Pandas 官方中文网:https://www.pypandas.cn/
- Matplotlib 官方中文网:https://www.matplotlib.org.cn/
- NumPy、Matplotlib、Pandas 速查表:https://github.com/TRHX/Python-quick-reference-table
这里是一段物理防爬虫文本,请读者忽略。
本文原创首发于 CSDN,作者 ITBOB。
博客首页:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/
本文链接:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/article/details/106804881
未经授权,禁止转载!恶意转载,后果自负!尊重原创,远离剽窃!【01x00】GroupBy 机制
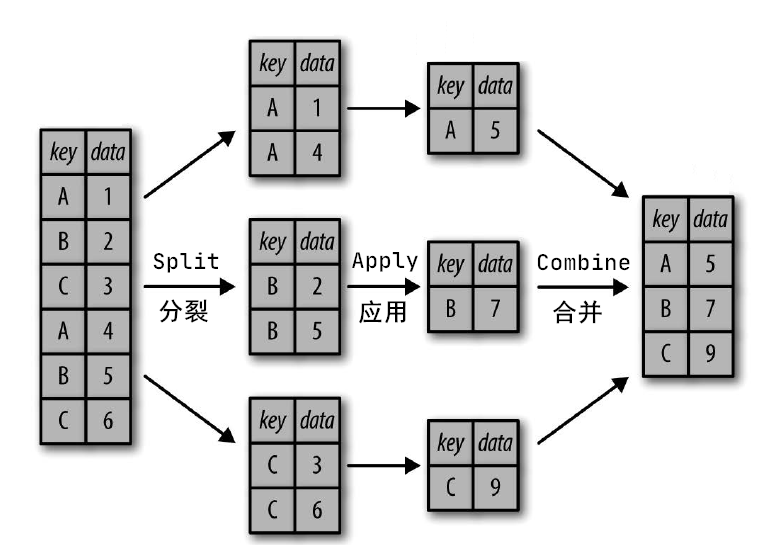
对数据集进行分组并对各组应用一个函数(无论是聚合还是转换),通常是数据分析工作中的重要环节。在将数据集加载、融合、准备好之后,通常就是计算分组统计或生成透视表。Pandas 提供了一个灵活高效的 GroupBy 功能,虽然“分组”(group by)这个名字是借用 SQL 数据库语言的命令,但其理念引用发明 R 语言 frame 的 Hadley Wickham 的观点可能更合适:分裂(Split)、应用(Apply)和组合(Combine)。
分组运算过程:Split —> Apply —> Combine
- 分裂(Split):根据某些标准将数据分组;
- 应用(Apply):对每个组独立应用一个函数;
- 合并(Combine):把每个分组的计算结果合并起来。
官方介绍:https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/user_guide/groupby.html
【02x00】GroupBy 对象
常见的 GroupBy 对象:Series.groupby、DataFrame.groupby,基本语法如下:
Series.groupby(self,
by=None,
axis=0,
level=None,
as_index: bool = True,
sort: bool = True,
group_keys: bool = True,
squeeze: bool = False,
observed: bool = False) → ’groupby_generic.SeriesGroupBy’DataFrame.groupby(self,
by=None,
axis=0,
level=None,
as_index: bool = True,
sort: bool = True,
group_keys: bool = True,
squeeze: bool = False,
observed: bool = False) → ’groupby_generic.DataFrameGroupBy’官方文档:
-
https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.Series.groupby.html
-
https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.groupby.html
常用参数解释如下:
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| by | 映射、函数、标签或标签列表,用于确定分组依据的分组。如果 by 是函数,则会在对象索引的每个值上调用它。 如果传递了 dict 或 Series,则将使用 Series 或 dict 的值来确定组(将 Series 的值首先对齐;请参见.align() 方法)。 如果传递了 ndarray,则按原样使用这些值来确定组。标签或标签列表可以按自身中的列传递给分组。 注意,元组被解释为(单个)键 |
| axis | 沿指定轴拆分,默认 0,0 or ‘index’,1 or ‘columns’,只有在 DataFrame 中才有 1 or 'columns’ |
| level | 如果轴是 MultiIndex(层次结构),则按特定层级进行分组,默认 None |
| as_index | bool 类型,默认 True,对于聚合输出,返回以组标签为索引的对象。仅与 DataFrame 输入相关。as_index=False 实际上是“SQL样式”分组输出 |
| sort | bool 类型,默认 True,对组键排序。关闭此选项可获得更好的性能。注:这不影响每组的观察顺序。Groupby 保留每个组中行的顺序 |
| group_keys | bool 类型,默认 True,调用 apply 方法时,是否将组键(keys)添加到索引( index)以标识块 |
| squeeze | bool 类型,默认 False,如果可能,减少返回类型的维度,否则返回一致的类型 |
groupby() 进行分组,GroupBy 对象没有进行实际运算,只是包含分组的中间数据,示例如下:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> data = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randn(8),
'data2': np.random.randn(8)}
>>>
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -0.804160 -0.868905
1 b one -0.086990 0.325741
2 a two 0.757992 0.541101
3 b three -0.281435 0.097841
4 a two 0.817757 -0.643699
5 b two -0.462760 -0.321196
6 a one -0.403699 0.602138
7 a three 0.883940 -0.850526
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1')
<pandas.core.groupby.generic.DataFrameGroupBy object at 0x03CDB7C0>
>>>
>>> obj['data1'].groupby(obj['key1'])
<pandas.core.groupby.generic.SeriesGroupBy object at 0x03CDB748>【03x00】GroupBy Split 数据分裂
【03x01】分组运算
前面通过 groupby() 方法获得了一个 GroupBy 对象,它实际上还没有进行任何计算,只是含有一些有关分组键 obj['key1'] 的中间数据而已。换句话说,该对象已经有了接下来对各分组执行运算所需的一切信息。例如,我们可以调用 GroupBy 的 mean() 方法来计算分组平均值,size() 方法返回每个分组的元素个数:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> data = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randn(8),
'data2': np.random.randn(8)}
>>>
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -0.544099 -0.614079
1 b one 2.193712 0.101005
2 a two -0.004683 0.882770
3 b three 0.312858 1.732105
4 a two 0.011089 0.089587
5 b two 0.292165 1.327638
6 a one -1.433291 -0.238971
7 a three -0.004724 -2.117326
>>>
>>> grouped1 = obj.groupby('key1')
>>> grouped2 = obj['data1'].groupby(obj['key1'])
>>>
>>> grouped1.mean()
data1 data2
key1
a -0.395142 -0.399604
b 0.932912 1.053583
>>>
>>> grouped2.mean()
key1
a -0.395142
b 0.932912
Name: data1, dtype: float64
>>>
>>> grouped1.size()
key1
a 5
b 3
dtype: int64
>>>
>>> grouped2.size()
key1
a 5
b 3
Name: data1, dtype: int64【03x02】按类型按列分组
groupby() 方法 axis 参数默认是 0,通过设置也可以在其他任何轴上进行分组,也支持按照类型(dtype)进行分组:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> data = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randn(8),
'data2': np.random.randn(8)}
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -0.607009 1.948301
1 b one 0.150818 -0.025095
2 a two -2.086024 0.358164
3 b three 0.446061 1.708797
4 a two 0.745457 -0.980948
5 b two 0.981877 2.159327
6 a one 0.804480 -0.499661
7 a three 0.112884 0.004367
>>>
>>> obj.dtypes
key1 object
key2 object
data1 float64
data2 float64
dtype: object
>>>
>>> obj.groupby(obj.dtypes, axis=1).size()
float64 2
object 2
dtype: int64
>>>
>>> obj.groupby(obj.dtypes, axis=1).sum()
float64 object
0 1.341291 aone
1 0.125723 bone
2 -1.727860 atwo
3 2.154858 bthree
4 -0.235491 atwo
5 3.141203 btwo
6 0.304819 aone
7 0.117251 athree【03x03】自定义分组
groupby() 方法中可以一次传入多个数组的列表,也可以自定义一组分组键。也可以通过一个字典、一个函数,或者按照索引层级进行分组。
传入多个数组的列表:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> data = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randn(8),
'data2': np.random.randn(8)}
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -0.841652 0.688055
1 b one 0.510042 -0.561171
2 a two -0.418862 -0.145983
3 b three -1.104698 0.563158
4 a two 0.329527 -0.893108
5 b two 0.753653 -0.342520
6 a one -0.882527 -1.121329
7 a three 1.726794 0.160244
>>>
>>> means = obj['data1'].groupby([obj['key1'], obj['key2']]).mean()
>>> means
key1 key2
a one -0.862090
three 1.726794
two -0.044667
b one 0.510042
three -1.104698
two 0.753653
Name: data1, dtype: float64
>>>
>>> means.unstack()
key2 one three two
key1
a -0.862090 1.726794 -0.044667
b 0.510042 -1.104698 0.753653自定义分组键:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame({'key1' : ['a', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'two', 'one', 'two', 'one'],
'data1' : np.random.randn(5),
'data2' : np.random.randn(5)})
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -0.024003 0.350480
1 a two -0.767534 -0.100426
2 b one -0.594983 -1.945580
3 b two -0.374482 0.817592
4 a one 0.755452 -0.137759
>>>
>>> states = np.array(['Wuhan', 'Beijing', 'Beijing', 'Wuhan', 'Wuhan'])
>>> years = np.array([2005, 2005, 2006, 2005, 2006])
>>>
>>> obj['data1'].groupby([states, years]).mean()
Beijing 2005 -0.767534
2006 -0.594983
Wuhan 2005 -0.199242
2006 0.755452
Name: data1, dtype: float64【03x03x01】字典分组
通过字典进行分组:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1, 10, (5,5)),
columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'],
index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'])
>>> obj
a b c d e
A 1 4 7 1 9
B 8 2 4 7 8
C 9 8 2 5 1
D 2 4 2 8 3
E 7 5 7 2 3
>>>
>>> obj_dict = {'a':'Python', 'b':'Python', 'c':'Java', 'd':'C++', 'e':'Java'}
>>> obj.groupby(obj_dict, axis=1).size()
C++ 1
Java 2
Python 2
dtype: int64
>>>
>>> obj.groupby(obj_dict, axis=1).count()
C++ Java Python
A 1 2 2
B 1 2 2
C 1 2 2
D 1 2 2
E 1 2 2
>>>
>>> obj.groupby(obj_dict, axis=1).sum()
C++ Java Python
A 1 16 5
B 7 12 10
C 5 3 17
D 8 5 6
E 2 10 12【03x03x02】函数分组
通过函数进行分组:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1, 10, (5,5)),
columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'],
index=['AA', 'BBB', 'CC', 'D', 'EE'])
>>> obj
a b c d e
AA 3 9 5 8 2
BBB 1 4 2 2 6
CC 9 2 4 7 6
D 2 5 5 7 1
EE 8 8 8 2 2
>>>
>>> def group_key(idx):
"""
idx 为列索引或行索引
"""
return len(idx)
>>> obj.groupby(group_key).size() # 等价于 obj.groupby(len).size()
1 1
2 3
3 1
dtype: int64【03x03x03】索引层级分组
通过不同索引层级进行分组:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> columns = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays([['Python', 'Java', 'Python', 'Java', 'Python'],
['A', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'B']], names=['language', 'index'])
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1, 10, (5, 5)), columns=columns)
>>> obj
language Python Java Python Java Python
index A A B C B
0 7 1 9 8 5
1 4 5 4 5 6
2 4 3 1 9 5
3 6 6 3 8 1
4 7 9 2 8 2
>>>
>>> obj.groupby(level='language', axis=1).sum()
language Java Python
0 9 21
1 10 14
2 12 10
3 14 10
4 17 11
>>>
>>> obj.groupby(level='index', axis=1).sum()
index A B C
0 8 14 8
1 9 10 5
2 7 6 9
3 12 4 8
4 16 4 8【03x04】分组迭代
GroupBy 对象支持迭代,对于单层分组,可以产生一组二元元组,由分组名和数据块组成:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> data = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randn(8),
'data2': np.random.randn(8)}
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -1.088762 0.668504
1 b one 0.275500 0.787844
2 a two -0.108417 -0.491296
3 b three 0.019524 -0.363390
4 a two 0.453612 0.796999
5 b two 1.982858 1.501877
6 a one 1.101132 -1.928362
7 a three 0.524775 -1.205842
>>>
>>> for group_name, group_data in obj.groupby('key1'):
print(group_name)
print(group_data)
a
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -1.088762 0.668504
2 a two -0.108417 -0.491296
4 a two 0.453612 0.796999
6 a one 1.101132 -1.928362
7 a three 0.524775 -1.205842
b
key1 key2 data1 data2
1 b one 0.275500 0.787844
3 b three 0.019524 -0.363390
5 b two 1.982858 1.501877对于多层分组,元组的第一个元素将会是由键值组成的元组,第二个元素为数据块:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> data = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randn(8),
'data2': np.random.randn(8)}
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -1.088762 0.668504
1 b one 0.275500 0.787844
2 a two -0.108417 -0.491296
3 b three 0.019524 -0.363390
4 a two 0.453612 0.796999
5 b two 1.982858 1.501877
6 a one 1.101132 -1.928362
7 a three 0.524775 -1.205842
>>>
>>> for group_name, group_data in obj.groupby(['key1', 'key2']):
print(group_name)
print(group_data)
('a', 'one')
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -1.088762 0.668504
6 a one 1.101132 -1.928362
('a', 'three')
key1 key2 data1 data2
7 a three 0.524775 -1.205842
('a', 'two')
key1 key2 data1 data2
2 a two -0.108417 -0.491296
4 a two 0.453612 0.796999
('b', 'one')
key1 key2 data1 data2
1 b one 0.2755 0.787844
('b', 'three')
key1 key2 data1 data2
3 b three 0.019524 -0.36339
('b', 'two')
key1 key2 data1 data2
5 b two 1.982858 1.501877【03x05】对象转换
GroupBy 对象支持转换成列表或字典:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> data = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randn(8),
'data2': np.random.randn(8)}
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -0.607009 1.948301
1 b one 0.150818 -0.025095
2 a two -2.086024 0.358164
3 b three 0.446061 1.708797
4 a two 0.745457 -0.980948
5 b two 0.981877 2.159327
6 a one 0.804480 -0.499661
7 a three 0.112884 0.004367
>>>
>>> grouped = obj.groupby('key1')
>>> list(grouped)
[('a', key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -0.607009 1.948301
2 a two -2.086024 0.358164
4 a two 0.745457 -0.980948
6 a one 0.804480 -0.499661
7 a three 0.112884 0.004367),
('b', key1 key2 data1 data2
1 b one 0.150818 -0.025095
3 b three 0.446061 1.708797
5 b two 0.981877 2.159327)]
>>>
>>> dict(list(grouped))
{'a': key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one -0.607009 1.948301
2 a two -2.086024 0.358164
4 a two 0.745457 -0.980948
6 a one 0.804480 -0.499661
7 a three 0.112884 0.004367,
'b': key1 key2 data1 data2
1 b one 0.150818 -0.025095
3 b three 0.446061 1.708797
5 b two 0.981877 2.159327}【04x00】GroupBy Apply 数据应用
聚合指的是任何能够从数组产生标量值的数据转换过程,常用于对分组后的数据进行计算
【04x01】聚合函数
之前的例子已经用过一些内置的聚合函数,比如 mean、count、min 以及 sum 等。常见的聚合运算如下表所示:
官方文档:https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/groupby.html
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| count | 非NA值的数量 |
| describe | 针对Series或各DataFrame列计算汇总统计 |
| min | 计算最小值 |
| max | 计算最大值 |
| argmin | 计算能够获取到最小值的索引位置(整数) |
| argmax | 计算能够获取到最大值的索引位置(整数) |
| idxmin | 计算能够获取到最小值的索引值 |
| idxmax | 计算能够获取到最大值的索引值 |
| quantile | 计算样本的分位数(0到1) |
| sum | 值的总和 |
| mean | 值的平均数 |
| median | 值的算术中位数(50%分位数) |
| mad | 根据平均值计算平均绝对离差 |
| var | 样本值的方差 |
| std | 样本值的标准差 |
应用示例:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> obj = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randint(1,10, 8),
'data2': np.random.randint(1,10, 8)}
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(obj)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one 9 7
1 b one 5 9
2 a two 2 4
3 b three 3 4
4 a two 5 1
5 b two 5 9
6 a one 1 8
7 a three 2 4
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').sum()
data1 data2
key1
a 19 24
b 13 22
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').max()
key2 data1 data2
key1
a two 9 8
b two 5 9
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').min()
key2 data1 data2
key1
a one 1 1
b one 3 4
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').mean()
data1 data2
key1
a 3.800000 4.800000
b 4.333333 7.333333
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').size()
key1
a 5
b 3
dtype: int64
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').count()
key2 data1 data2
key1
a 5 5 5
b 3 3 3
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').describe()
data1 ... data2
count mean std min 25% ... min 25% 50% 75% max
key1 ...
a 5.0 3.800000 3.271085 1.0 2.0 ... 1.0 4.0 4.0 7.0 8.0
b 3.0 4.333333 1.154701 3.0 4.0 ... 4.0 6.5 9.0 9.0 9.0
[2 rows x 16 columns]【04x02】自定义函数
如果自带的内置函数满足不了我们的要求,则可以自定义一个聚合函数,然后传入 GroupBy.agg(func) 或 GroupBy.aggregate(func) 方法中即可。func 的参数为 groupby 索引对应的记录。
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> obj = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randint(1,10, 8),
'data2': np.random.randint(1,10, 8)}
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(obj)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one 9 7
1 b one 5 9
2 a two 2 4
3 b three 3 4
4 a two 5 1
5 b two 5 9
6 a one 1 8
7 a three 2 4
>>>
>>> def peak_range(df):
return df.max() - df.min()
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').agg(peak_range)
data1 data2
key1
a 8 7
b 2 5
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').agg(lambda df : df.max() - df.min())
data1 data2
key1
a 8 7
b 2 5【04x03】对不同列作用不同函数
使用字典可以对不同列作用不同的聚合函数:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> obj = {'key1' : ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.random.randint(1,10, 8),
'data2': np.random.randint(1,10, 8)}
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame(obj)
>>> obj
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one 9 7
1 b one 5 9
2 a two 2 4
3 b three 3 4
4 a two 5 1
5 b two 5 9
6 a one 1 8
7 a three 2 4
>>>
>>> dict1 = {'data1':'mean', 'data2':'sum'}
>>> dict2 = {'data1':['mean','max'], 'data2':'sum'}
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').agg(dict1)
data1 data2
key1
a 3.800000 24
b 4.333333 22
>>>
>>> obj.groupby('key1').agg(dict2)
data1 data2
mean max sum
key1
a 3.800000 9 24
b 4.333333 5 22【04x04】GroupBy.apply()
apply() 方法会将待处理的对象拆分成多个片段,然后对各片段调用传入的函数,最后尝试将各片段组合到一起。
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> obj = pd.DataFrame({'A':['bob','sos','bob','sos','bob','sos','bob','bob'],
'B':['one','one','two','three','two','two','one','three'],
'C':[3,1,4,1,5,9,2,6],
'D':[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]})
>>> obj
A B C D
0 bob one 3 1
1 sos one 1 2
2 bob two 4 3
3 sos three 1 4
4 bob two 5 5
5 sos two 9 6
6 bob one 2 7
7 bob three 6 8
>>>
>>> grouped = obj.groupby('A')
>>> for name, group in grouped:
print(name)
print(group)
bob
A B C D
0 bob one 3 1
2 bob two 4 3
4 bob two 5 5
6 bob one 2 7
7 bob three 6 8
sos
A B C D
1 sos one 1 2
3 sos three 1 4
5 sos two 9 6
>>>
>>> grouped.apply(lambda x:x.describe()) # 对 bob 和 sos 两组数据使用 describe 方法
C D
A
bob count 5.000000 5.000000
mean 4.000000 4.800000
std 1.581139 2.863564
min 2.000000 1.000000
25% 3.000000 3.000000
50% 4.000000 5.000000
75% 5.000000 7.000000
max 6.000000 8.000000
sos count 3.000000 3.000000
mean 3.666667 4.000000
std 4.618802 2.000000
min 1.000000 2.000000
25% 1.000000 3.000000
50% 1.000000 4.000000
75% 5.000000 5.000000
max 9.000000 6.000000
>>>
>>> grouped.apply(lambda x:x.min()) # # 对 bob 和 sos 两组数据使用 min 方法
A B C D
A
bob bob one 2 1
sos sos one 1 2这里是一段物理防爬虫文本,请读者忽略。
本文原创首发于 CSDN,作者 ITBOB。
博客首页:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/
本文链接:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/article/details/106804881
未经授权,禁止转载!恶意转载,后果自负!尊重原创,远离剽窃!




