Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(二):文本描述/中文支持/画布/网格等基本图像属性
文章目录
Matplotlib 系列文章:
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(一):初识 Matplotlib 与其 matplotibrc 配置文件
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(二):文本描述 / 中文支持 / 画布 / 网格等基本图像属性
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(三):图例 / LaTeX / 刻度 / 子图 / 补丁等基本图像属性
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(四):线性图的绘制
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(五):散点图的绘制
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(六):直方图 / 柱状图 / 条形图的绘制
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(七):饼状图的绘制
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(八):等高线 / 等值线图的绘制
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(九):极区图 / 极坐标图 / 雷达图的绘制
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(十):3D 图的绘制
- Python 数据分析三剑客之 Matplotlib(十一):最热门最常用的 50 个图表【译文】
专栏:
- NumPy 专栏:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/category_9780393.html
- Pandas 专栏:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/category_9780397.html
- Matplotlib 专栏:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/category_9780418.html
推荐学习资料与网站:
- NumPy 官方中文网:https://www.numpy.org.cn/
- Pandas 官方中文网:https://www.pypandas.cn/
- Matplotlib 官方中文网:https://www.matplotlib.org.cn/
- NumPy、Matplotlib、Pandas 速查表:https://github.com/TRHX/Python-quick-reference-table
这里是一段物理防爬虫文本,请读者忽略。
本文原创首发于 CSDN,作者 ITBOB。
博客首页:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/
本文链接:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/article/details/105828049
未经授权,禁止转载!恶意转载,后果自负!尊重原创,远离剽窃!【1x00】添加文本描述
【1x01】添加标题:matplotlib.pyplot.title()
matplotlib.pyplot.title() 方法可为图表添加标题。
基本语法:matplotlib.pyplot.title(label[, fontdict=None, loc=None, pad=None])
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| label | str 类型,标题文字 |
| fontdict | 字典类型,控制标题文本外观,可选项,默认值为:{'fontsize': rcParams['axes.titlesize'], 'fontweight' : rcParams['axes.titleweight'], 'color' : rcParams['axes.titlecolor'], 'verticalalignment': 'baseline', 'horizontalalignment': loc} |
| loc | str 类型,可选项,三个可选值:center、left、right,默认为 rcParams["axes.titlelocation"](默认为 center) |
| pad | float 类型,可选项,标题距轴顶部的偏移量(以磅为单位)。如果为 None,则默认为 rcParams["axes.titlepad"](默认为:6.0) |
应用举例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = range(2, 26, 2)
y = range(0, 12)
plt.title('This is a title')
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.show()
【1x02】为坐标轴添加标签:matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel() / ylabel()
matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel():为 x 轴添加标签;
matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel():为 y 轴添加标签。
基本语法:
matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel(xlabel[, fontdict=None, labelpad=None])
matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel(ylabel[, fontdict=None, labelpad=None])
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| xlabel / ylabel | str 类型,要添加的文本信息 |
| fontdict | 字典类型,控制标题文本外观,可选项,默认值为:{'fontsize': rcParams['axes.titlesize'], 'fontweight' : rcParams['axes.titleweight'], 'color' : rcParams['axes.titlecolor'], 'verticalalignment': 'baseline', 'horizontalalignment': loc} |
| labelpad | float 类型,可选项,x 轴标签距离 x 轴的距离 |
应用举例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = range(2, 26, 2)
y = range(0, 12)
a = [5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30]
b = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
plt.title('This is a title')
plt.xlabel('This is x label', fontdict={'fontsize': 15, 'fontweight': 'bold', 'color': 'red'}, labelpad=15.0)
plt.ylabel('This is y label', fontsize=10, fontweight='light', color='blue', labelpad=15.0)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.plot(a, b)
plt.show()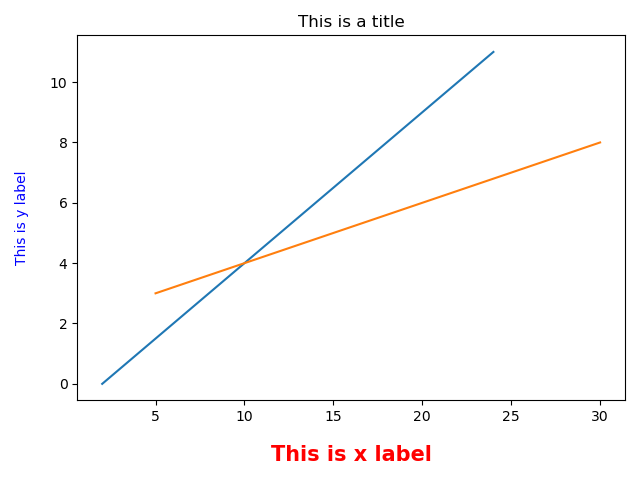
【1x03】任意位置添加文本:matplotlib.pyplot.text()
matplotlib.pyplot.text() 方法可以在画布上任意位置添加文本描述。
基本语法:matplotlib.pyplot.text(x, y, s[, fontdict=None, withdash=<deprecated parameter>])
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| x, y | 放置文本的坐标位置 |
| s | str 类型,要添加的文本信息 |
| fontdict | 字典类型,控制标题文本外观,可选项,默认值为:{'fontsize': rcParams['axes.titlesize'], 'fontweight' : rcParams['axes.titleweight'], 'color' : rcParams['axes.titlecolor'], 'verticalalignment': 'baseline', 'horizontalalignment': loc} |
| ha | 注释点在注释文本的左边、右边或中间(left、right、center) |
| va | 注释点在注释文本的上边、下边、中间或基线 (top、bottom、center、baseline) |
| withdash | bool 类型,可选项,默认为 False,创建一个 TextWithDash 实例而不是一个 Text 实例 |
应用举例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['lines.marker'] = 'o' # 设置线条上点的形状
a = [5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30]
b = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
plt.title('This is a title')
plt.xlabel('This is x label')
plt.ylabel('This is y label')
plt.text(4, 3.2, 'text1')
plt.text(9, 4.2, 'text2')
plt.text(14, 5.2, 'text3')
plt.text(19, 6.2, 'text4')
plt.text(24, 7.2, 'text5')
plt.text(27.5, 7.9, 'text6')
plt.plot(a, b)
plt.show()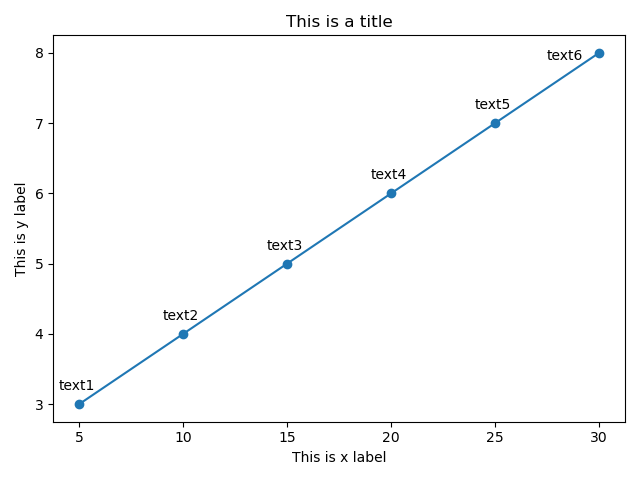
【1x03】任意位置添加文本:matplotlib.pyplot.annotate()
matplotlib.pyplot.annotate() 方法可以在指定坐标点添加文本或 LaTeX 描述,也可以在其他位置添加描述后,使用箭头指向某个坐标点。比 matplotlib.pyplot.text() 更高级。
基本语法:matplotlib.pyplot.annotate(text, xy, xytext, xycoords, textcoords, ha, va, arrowprops, \*\*kwargs)
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| text | str 类型,注释的文本 |
| xy | 被注释的坐标点,格式:(x, y) |
| xytext | 注释文本的坐标点,格式:(x, y),默认与 xy 相同 |
| xycoords | 被注释的坐标点的参考系,取值参见表一,默认为 ‘data’ |
| textcoords | 注释文本的坐标点的参考系,取值参见表二,默认为 xycoords 的值 |
| ha | 注释点在注释文本的左边、右边或中间(left、right、center) |
| va | 注释点在注释文本的上边、下边、中间或基线 (top、bottom、center、baseline) |
| arrowprops | dict 字典类型,箭头的样式 如果 arrowprops 不包含键 arrowstyle,则允许的键参见表三 如果 arrowprops 包含键 arrowstyle,则允许的键参见表四 |
| 表一:xycoords 取值类型 |
| 取值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ‘figure points’ | 以画布左下角为参考,单位为点数 |
| ‘figure pixels’ | 以画布左下角为参考,单位为像素 |
| ‘figure fraction’ | 以画布左下角为参考,单位为百分比 |
| ‘axes points’ | 以绘图区左下角为参考,单位为点数 |
| ‘axes pixels’ | 以绘图区左下角为参考,单位为像素 |
| ‘axes fraction’ | 以绘图区左下角为参考,单位为百分比 |
| ‘data’ | 使用被注释对象的坐标系,即数据的 x, y 轴(默认) |
| ‘polar’ | 使用(θ,r)形式的极坐标系 |
| 表二:textcoords 取值类型 |
| 取值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ‘figure points’ | 以画布左下角为参考,单位为点数 |
| ‘figure pixels’ | 以画布左下角为参考,单位为像素 |
| ‘figure fraction’ | 以画布左下角为参考,单位为百分比 |
| ‘axes points’ | 以绘图区左下角为参考,单位为点数 |
| ‘axes pixels’ | 以绘图区左下角为参考,单位为像素 |
| ‘axes fraction’ | 以绘图区左下角为参考,单位为百分比 |
| ‘data’ | 使用被注释对象的坐标系,即数据的 x, y 轴 |
| ‘polar’ | 使用(θ,r)形式的极坐标系 |
| ‘offset points’ | 相对于被注释点的坐标 xy 的偏移量,单位是点 |
| ‘offset pixels’ | 相对于被注释点的坐标 xy 的偏移量,单位是像素 |
| 表三:arrowprops 不包含键 arrowstyle 时的取值 |
| 键 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| width | 箭头的宽度,以点为单位 |
| headwidth | 箭头底部的宽度,以点为单位 |
| headlength | 箭头的长度,以点为单位 |
| shrink | 箭头两端收缩占总长的百分比 |
| ? | 其他 matplotlib.patches.FancyArrowPatch 中的关键字,部分常用关键字参见表五 |
| 表四:arrowprops 包含键 arrowstyle 时的取值 |
| 取值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
'-' |
None |
'->' |
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2 |
'-[' |
widthB=1.0,lengthB=0.2,angleB=None |
']-' |
widthA=1.0, lengthA=0.2, angleA=None |
]-[ |
widthA=1.0, lengthA=0.2, angleA=None, widthB=1.0, lengthB=0.2, angleB=None |
| `’ | - |
| `'- | >'` |
'<-' |
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2 |
'<->' |
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2 |
| `'< | -'` |
| `'< | - |
'fancy' |
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.4,tail_width=0.4 |
'simple' |
head_length=0.5,head_width=0.5,tail_width=0.2 |
'wedge' |
tail_width=0.3,shrink_factor=0.5 |
| 表五:matplotlib.patches.FancyArrowPatch 常用的键 |
| 键 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| arrowstyle | 箭头样式,取值参见表四 |
| connectionstyle | 连接方式,默认为 arc3,有以下五种取值:angle:angleA=90, angleB=0, rad=0.0angle3:angleA=90, angleB=0arc:angleA=0, angleB=0, armA=None, armB=None, rad=0.0arc3:rad=0.0bar:armA=0.0, armB=0.0, fraction=0.3, angle=Noneangle 为箭头旋转的角度,rad 为弧度 |
| relpos | 箭头起始点相对注释文本的位置,默认为 (0.5, 0.5),即文本的中心 (0,0)表示左下角,(1,1)表示右上角 |
| patchA | 箭头起点处的图形,默认为文本的边框 |
| patchB | 箭头终点处的图形,默认为空 |
| shrinkA | 箭头起点的缩进点数,默认为2 |
| shrinkB | 箭头终点的缩进点数,默认为2 |
| ? | 其他键值,参见官方文档 matplotlib.patches.PathPatch |
| connectionstyle 样式举例 |
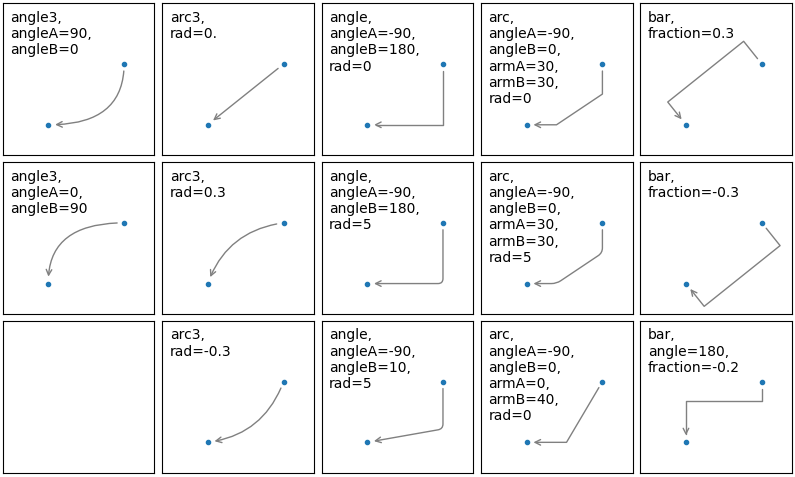
应用举例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(-2*np.pi, 2*np.pi, 0.01)
y = np.sin(1*x)/x
plt.title('This is a title')
plt.xlabel('This is x label')
plt.ylabel('This is y label')
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.annotate(r'$\lim_{x\to 0}\frac{\sin(x)}{x}=1$', # 插入 LaTeX 表达式
xy=[0, 1], # 被标记的坐标
xycoords='data', # 被标记的坐标的参考系
xytext=[50, -40], # 注释文本的坐标
textcoords='offset points', # 注释文本的坐标的参考系
fontsize=16, # 字体大小
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3, rad=.2")) # 箭头样式
plt.show()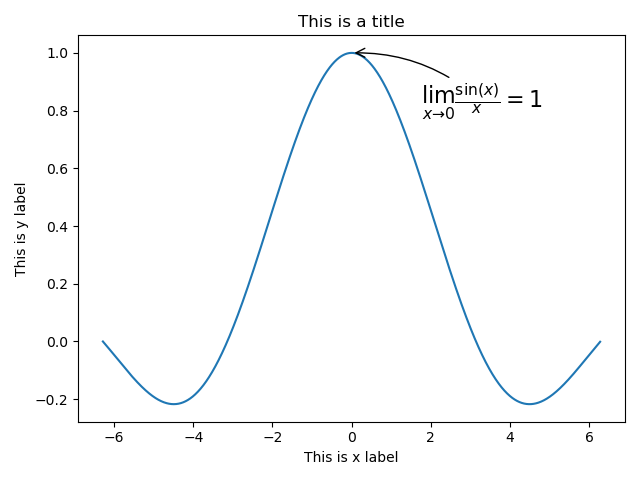
这里是一段物理防爬虫文本,请读者忽略。
本文原创首发于 CSDN,作者 ITBOB。
博客首页:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/
本文链接:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/article/details/105828049
未经授权,禁止转载!恶意转载,后果自负!尊重原创,远离剽窃!【2x00】设置中文显示
【2x01】常见系统自带文字及其英文名称
Windows 系统中常见自带字体:
| 字体 | 英文名称 |
|---|---|
| 黑体 | SimHei |
| 宋体 | SimSun |
| 新宋体 | NSimSun |
| 仿宋 | FangSong |
| 仿宋_GB2312 | FangSong_GB2312 |
| 楷体_GB2312 | KaiTi_GB2312 |
| 楷体 | KaiTi |
| 微软正黑 | Microsoft JhengHei |
| 微软雅黑 | Microsoft YaHei |
| 细明体 | MingLiU |
| 标楷体 | DFKai-SB |
| 新细明体 | PMingLiU |
装有 office 后新添加的字体:
| 字体 | 英文名称 |
|---|---|
| 隶书 | LiSu |
| 幼圆 | YouYuan |
| 华文细黑 | STXihei |
| 华文楷体 | STKaiti |
| 华文宋体 | STSong |
| 华文中宋 | STZhongsong |
| 华文仿宋 | STFangsong |
| 方正舒体 | FZShuTi |
| 方正姚体 | FZYaoti |
| 华文彩云 | STCaiyun |
| 华文琥珀 | STHupo |
| 华文隶书 | STLiti |
| 华文行楷 | STXingkai |
| 华文新魏 | STXinwei |
Mac OS 系统中常见自带字体:
| 字体 | 英文名称 |
|---|---|
| 华文细黑 | STHeiti Light / STXihei |
| 华文黑体 | STHeiti |
| 华文楷体 | STKaiti |
| 华文宋体 | STSong |
| 华文仿宋 | STFangsong |
| 丽黑 Pro | LiHei Pro Medium |
| 丽宋 Pro | LiSong Pro Light |
| 标楷体 | BiauKai |
| 苹果丽中黑 | Apple LiGothic Medium |
| 苹果丽细宋 | Apple LiSung Light |
【2x02】指定全局字体:rcParams
通过 rcParams['font.sans-serif'] 可以配置全局字体。
优点:只需设置一次即可显示所有中文;缺点:污染全局,无法对单个中文设置字体。
应用举例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Microsoft YaHei'] # 配置全局字体为微软雅黑
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 部分字体负号会显示乱码,可添加此参数进行配置
a = [-15, -10, -5, 20, 25, 30]
b = [-5, -4, -3, 6, 7, 8]
plt.title('这是中文标题')
plt.xlabel('这是 x 轴标签')
plt.ylabel('这是 y 轴标签')
plt.plot(a, b)
plt.show()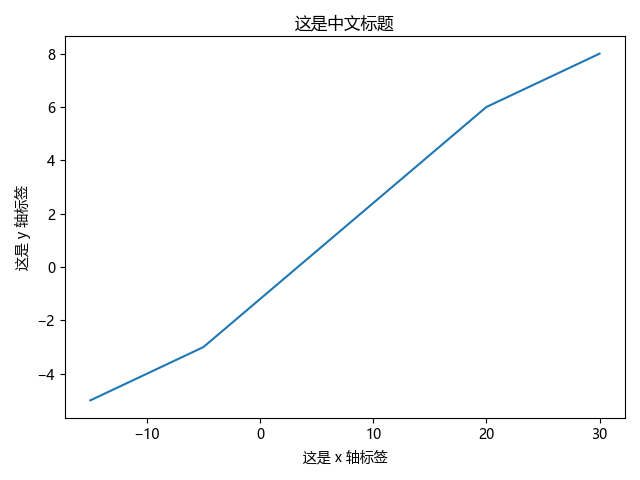
【2x03】指定单个字体:fontproperties
fontproperties 参数可以加在要设置中文的地方
优点:不污染全局;缺点:中文太多了挨个设置比较繁琐。
应用举例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
a = [-15, -10, -5, 20, 25, 30]
b = [-5, -4, -3, 6, 7, 8]
plt.title('这是中文标题', fontproperties='Microsoft JhengHei') # 微软正黑
plt.xlabel('这是 x 轴标签', fontproperties='STLiti') # 华文隶书
plt.ylabel('这是 y 轴标签', fontproperties='Microsoft YaHei') # 微软雅黑
plt.plot(a, b)
plt.show()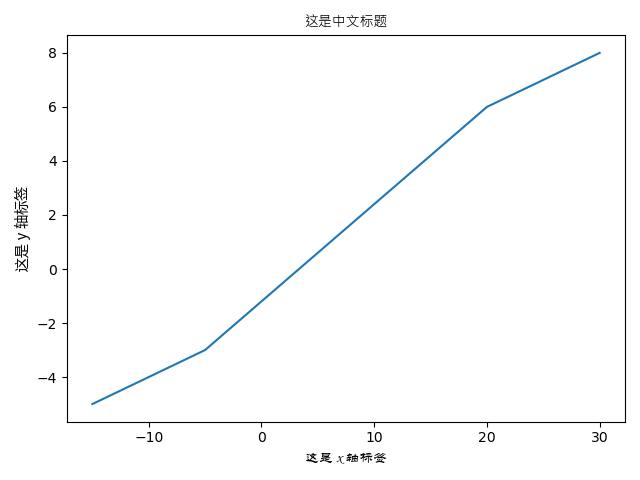
【2x04】指定文字路径:FontProperties
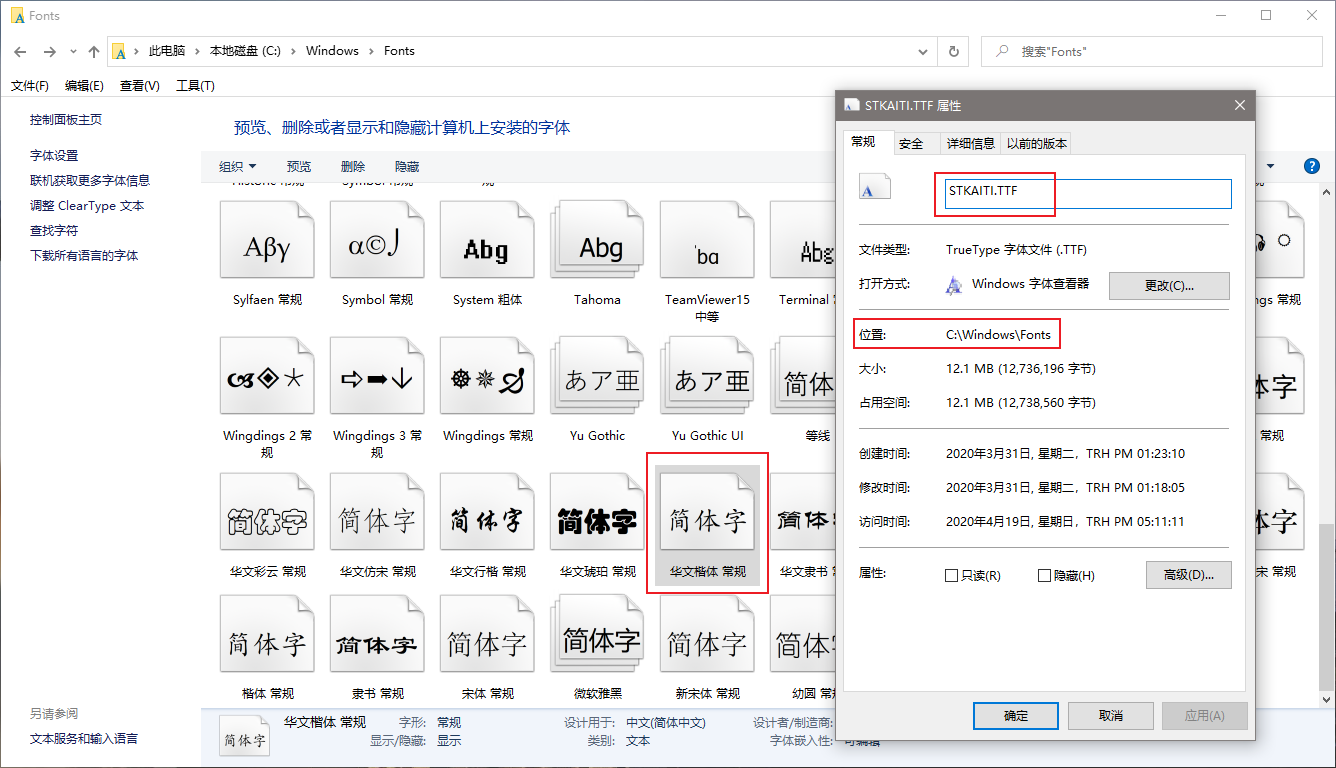
matplotlib 中 font_manager 模块的 FontProperties 方法可以通过指定文字路径来使用本地文字,在 Windows 中,文字路径一般是 C:\Windows\Fonts\,文字名称可以通过其属性来获取,部分用户自己安装的字体可能包含多个类型,可打开字体合集后通过其属性来获取。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r"C:\Windows\Fonts\STXINGKA.TTF", size=14)
a = [-15, -10, -5, 20, 25, 30]
b = [-5, -4, -3, 6, 7, 8]
plt.title('这是中文标题', fontproperties=font)
plt.xlabel('这是 x 轴标签', fontproperties=font)
plt.ylabel('这是 y 轴标签', fontproperties=font)
plt.plot(a, b)
plt.show()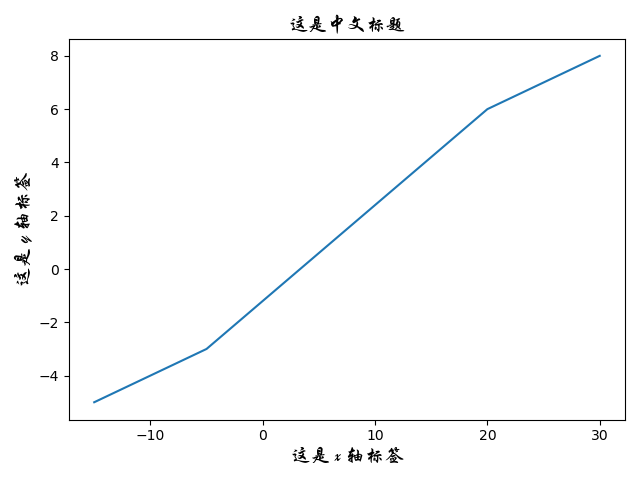
【2x05】文字更多属性:rc
rc 参数支持文字的更多属性设置,如字体粗细、大小等,这种方法同样将影响全局。
官方参考:https://matplotlib.org/api/matplotlib_configuration_api.html?highlight=rc#matplotlib.rc
应用举例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
font = {'family': 'SimHei',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': '10'}
plt.rc('font', **font) # 设置字体的更多属性
plt.rc('axes', unicode_minus=False) # 显示负号
a = [-15, -10, -5, 20, 25, 30]
b = [-5, -4, -3, 6, 7, 8]
plt.title('这是中文标题')
plt.xlabel('这是 x 轴标签')
plt.ylabel('这是 y 轴标签')
plt.plot(a, b)
plt.show()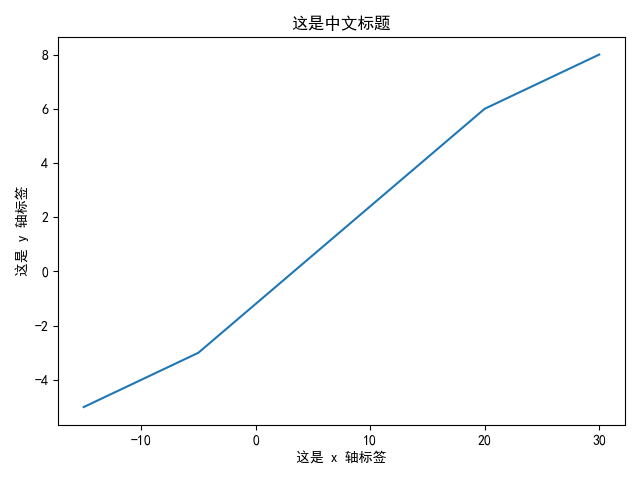
【3x00】设置画布大小 / 分辨率 / 颜色
matplotlib.pyplot.figure() 可以设置画布的大小、图片分辨率、颜色等。
基本语法:matplotlib.pyplot.figure(figsize=None, dpi=None, facecolor=None, edgecolor=None, frameon=True, \*\*kwargs)
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| figsize | (float, float) 的格式,代表宽度和高度,单位为英寸默认为 rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [6.4, 4.8],即:640 x 480 |
| dpi | 图像分辨率,默认为 rcParams["figure.figsize"] = 100 |
| facecolor | 图像背景颜色,默认为 rcParams["figure.edgecolor"] = ‘white’ |
| edgecolor | 图像边缘颜色,默认为 rcParams[’figure.edgecolor’] = ‘white’ |
| frameon | 是否启用图框 |
应用举例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Microsoft YaHei']
x = range(2, 26, 2)
y = range(0, 12)
plt.figure(figsize=(6.5, 5), dpi=120, facecolor='#BBFFFF')
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.show()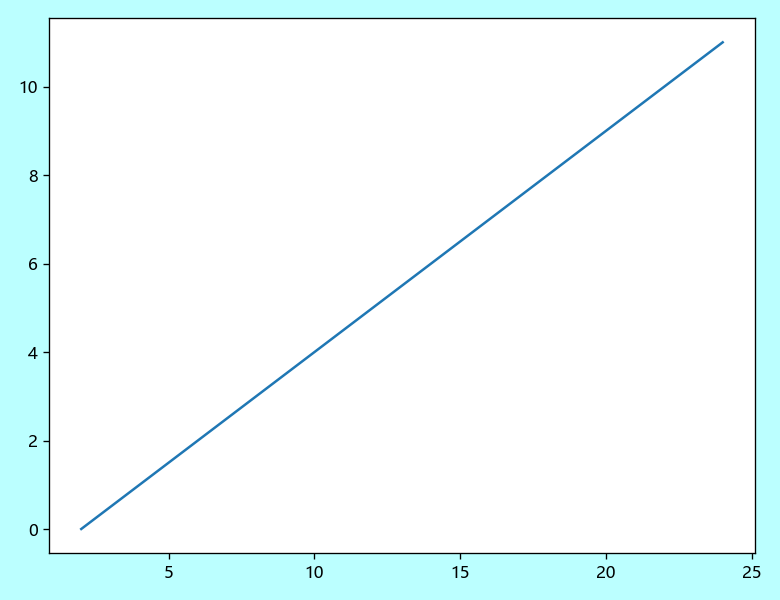
【4x00】设置网格
matplotlib.pyplot.grid() 方法可以为图表设置网格显示。
基本语法:matplotlib.pyplot.grid([b=None, which='major', axis='both', \*\*kwargs])
| 参数 | 属性 |
|---|---|
| b | bool 值,可选项,是否显示网格,值为 None 或 True 则显示,False 不显示 |
| which | 可选项,在主/次刻度显示网格线,major:主(大)刻度;minor:次(小)刻度;both:两者同时显示 |
| axis | 可选项,在横/竖轴显示网格线,x:x 轴;y:y 轴;both:两者同时显示 |
| **kwargs | 其他 Line2D 属性,常见 Line2D 属性见下表 |
Line2D 属性用法:grid(color='r', linestyle='-', linewidth=2),部分常见 Line2D 属性如下:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| alpha | 网格透明度,float 类型,取值范围:[0, 1],默认为 1.0,即不透明 |
| antialiased / aa | 是否使用抗锯齿渲染,默认为 True |
| color / c | 网格颜色,支持英文颜色名称及其简写、十六进制颜色码等,更多颜色示例参见官网 Color Demo |
| linestyle / ls | 网格线条样式:'-' or 'solid', '--' or 'dashed', '-.' or 'dashdot' ':' or 'dotted', 'none' or ' ' or '' |
| linewidth / lw | 网格线条宽度,float 类型,默认 0.8 |
应用举例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Microsoft YaHei']
a = [-15, -10, -5, 20, 25, 30]
b = [-5, -4, -3, 6, 7, 8]
plt.title('这是中文标题')
plt.xlabel('这是 x 轴标签')
plt.ylabel('这是 y 轴标签')
plt.grid(axis='x', color='red', linestyle='-.', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(a, b)
plt.show()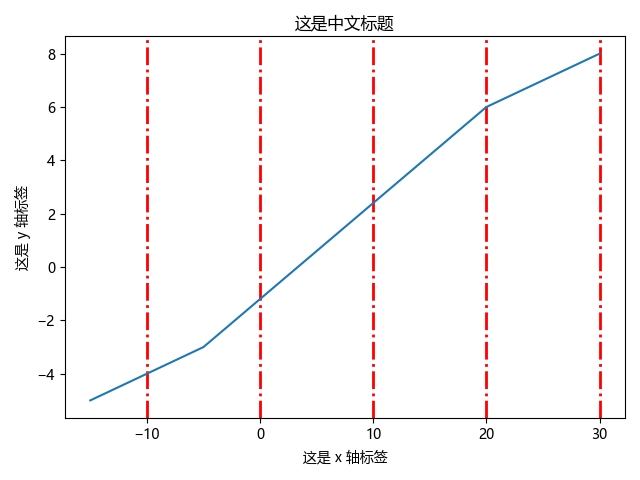
这里是一段物理防爬虫文本,请读者忽略。
本文原创首发于 CSDN,作者 ITBOB。
博客首页:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/
本文链接:https://itrhx.blog.csdn.net/article/details/105828049
未经授权,禁止转载!恶意转载,后果自负!尊重原创,远离剽窃!




